Hoffman's sign was positive in the left upper extremity ncbinlmnihgov see exam of spinal cord presentation ( Bertalanffy, et al ) 61% presented with radicular symptoms 16% had pure myelopathic symptoms 23% had a combination of myelopathic and radiculopathy upper motor neuron findings such as hyperreflexia, clonusThis is a positive Hoffman's test on a young lady who sustained a head injury in a motor vehicle accident Check out our new OEP merchandise https//wwwyoDegenerative myelopathy is the most common type of spinal cord dysfunction in patients older than 55 years The onset is usually subtle, with long periods of fixed disability and episodic worsening The first sign is commonly gait spasticity or difficulty in walking, followed by upper extremity numbness and loss of fine motor control in the hands
Cervical Myelopathy Physiopedia
How do you test for myelopathy
How do you test for myelopathy-Figure 3 Hoffmann signApr , 09 · cervical myelopathy, physical signs, myelopathic signs, long tract signs, hyperreflexia;



Lil Bone Peep Hoffmann S Sign Upper Motor Neuron Test Perform By Flicking Or Tapping The Nail While Relaxed Sign If The Thumb Index Finger Reflexively Adduct Flex
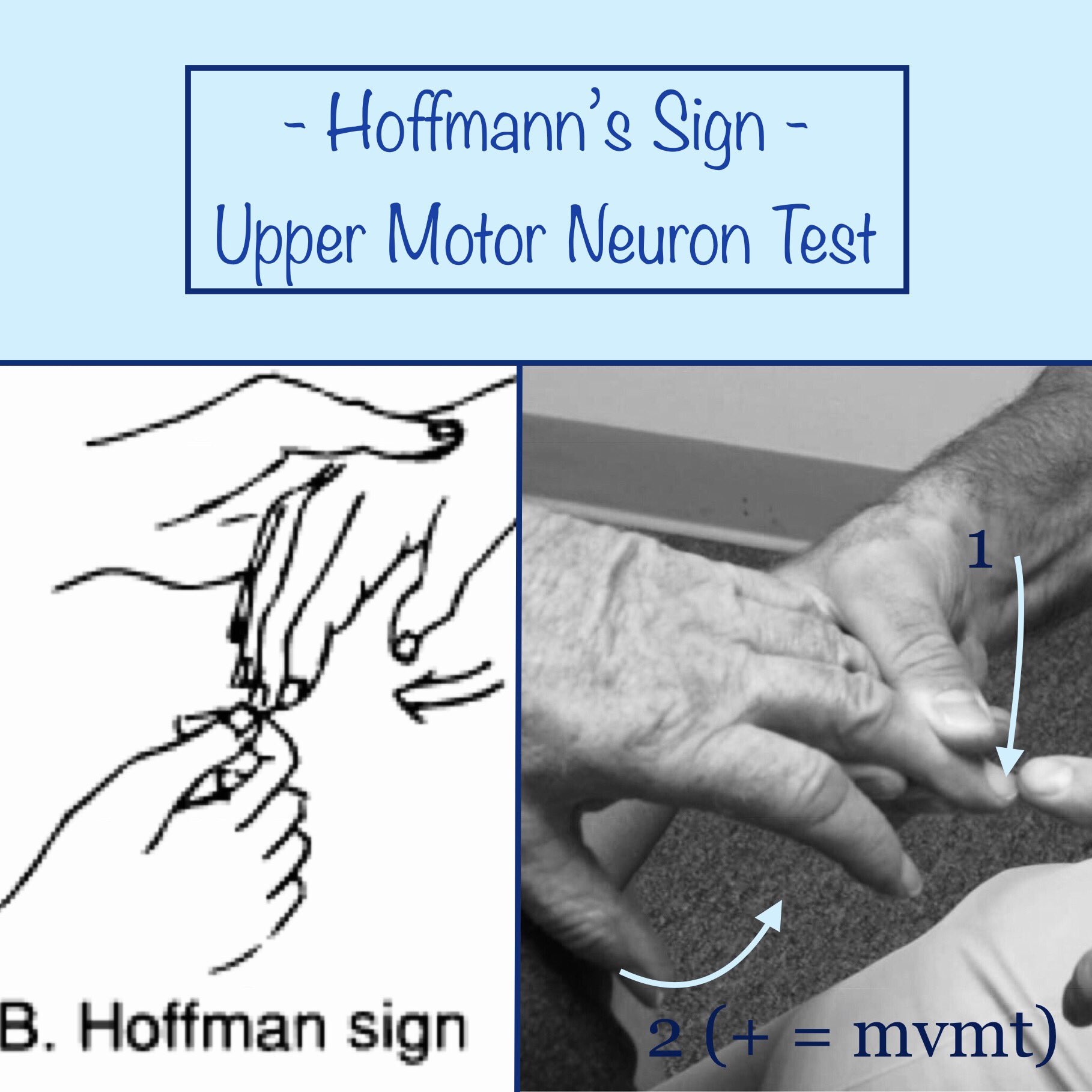
Sep 25, 17 · The Hoffman sign refers to the results of the Hoffman test This test is used to determine whether your fingers or thumbs flex involuntarily inClinical Test for cervical myelopathy / upper motor neuron pathologyIn patients surgically treated for cervical myelopathy, the Hoffmann sign is more prevalent and more likely to be seen in individuals with less severe neurological deficits than the Babinski sign In patients with lumbar symptoms, a bilateral Hoffmann sign was a
Hoffmann Sign More Prevalent Than Babinski Sign in Less Severe Neurological Deficits from Cervical Myelopathy Doctors have different techniques for assessing the neurological, or nerve, function in your body For example, when an infant is being examined during a wellbaby checkup, one thing that is performed is the Babinski sign or reflexA positive Hoffman's reflex may indicate an upper motor neuron lesion or a pyramidal sign Hoffmann's reflex may be seen in the following conditions Multiple sclerosis ALS Diseases which cause spinal cord compression (myelopathy) such as cervical spondylitis, tumors, or degenerative arthritisApr 14, 17 · Hoffman's Sign How You Get and What It Means He Hoffman sign Is an abnormal reflex response consisting of flexing the fingers of the hand by pressing the middle finger nail Although it is generally associated with pathologies such as pyramidal syndrome, it can occur in healthy people who have exalted reflexes (which is called hyperreflexia)
Hoffmann Sign is considered as a Red Flag for Cervical Myelopathy The Hoffmann sign is a reliable way to test for early signs of cervical myelopathy The presence of Hoffmann sign on both sides strongly suggests the presence of spinal cord compression in the cervical spine False positive and false negative Hoffman reflexJun 12, 18 · According to the Indian Journal of Medical Specialties, the Hoffman sign is more likely to occur in people with cervical myelopathy or injuries or damage to the cervical spine, which is the upperClonus, Babinski, inverted radial reflex, Hoffman sign Search for Similar Articles You may search for similar articles that contain these same keywords or you may modify the keyword list to augment your search




Common Cervical Spine Disorders Diagnosis And Treatment Wayne




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Common Cause Of Spinal Cord Dysfunction In Older Persons American Family Physician
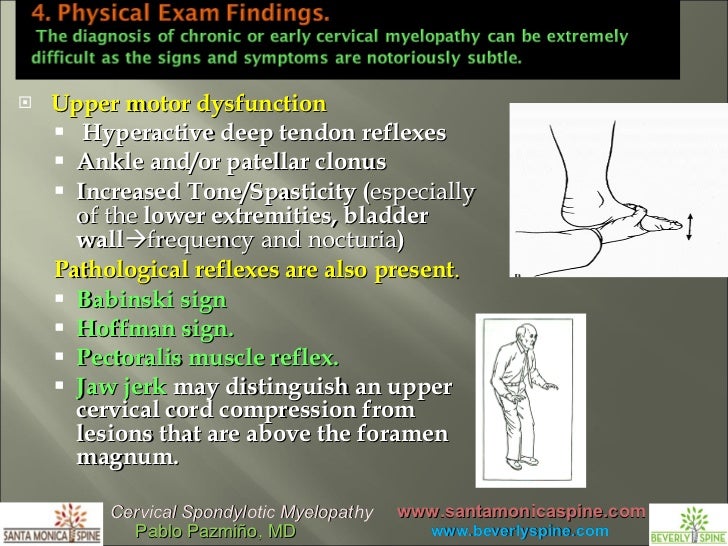
Sep 01, 00 · Cervical spondylotic myelopathy is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction in older persons The aging process results in degenerative changes in the cervical spine that, in advancedMar 01, 07 · The dynamic Hoffman is thought to correlate with a narrowed cervical canal and is felt to be an earlier clinical indicator of cervical spondylotic myelopathy than a typical Hoffman sign 29 Download Download highres image (769KB) Download Download fullsize image;Jan 01, 15 · Of the pathological reflexes, Hoffman sign has the strongest association with CSC, but still was only positive in 67% of cases More sensitive clinical measures need to be developed to more accurately associate CSC detected on MRI to the clinical severity of cervical spondylotic myelopathy Level of Evidence 4



Cervical Arthritis Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy By Pablo Pazmino




Cervical Myelopathy History And Physical Examination Sciencedirect
Hoffman's Sign definition Hoffman's sign can be a feature of myelopathy involving the cervical spinal cord It is a test performed by doctors during their neurological examinationObject The Hoffmann sign is commonly used in clinical practice to assess cervical spine disease It is unknown whether the sign correlates with the severity of myelopathy, and no consensus exists regarding the significance of a positive sign in asymptomatic individualsHoffmann's reflex (Hoffmann's sign, sometimes simply " Hoffmann's ", also finger flexor reflex) is a neurological examination finding elicited by a reflex test which can help verify the presence or absence of issues arising from the corticospinal tract It
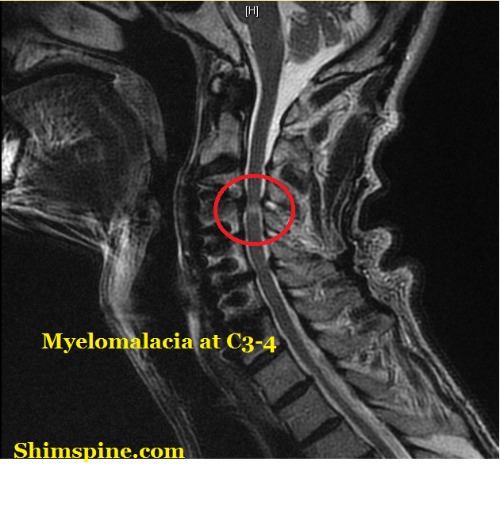



Hoffmann Sign And Myelopathy Shimspine




Cervical Arthritis Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Cervical Steno
Jun 28, · Hoffmann's sign is a test for pathological disorder in upper motor neuron reflex as seen in cervical myelopathy when the spinal cord in the cervical spine gets compressed and chances are that the patient will exhibit pathological reflexes The Hoffmann's sign is also known as a digital reflex, snapping reflex, Jacobson sign and trauma signFeb 22, 18 · Degenerative cervical myelopathy (DCM), earlier referred to as cervical spondylotic myelopathy, involves spinal cord dysfunction from compression in the neck 1 Patients report neurological symptoms such as pain and numbness in limbs, poor coordination, imbalance, and bladder problems Owing to its mobility, the vertebral column of the neck isMar 01, · The Hoffman sign has a prevalence of 2% in the general population, although a positive predictive value of 68% and negative predictive value of 70% for CSM make it a useful adjunct in diagnosis 33,34 Sensory changes due to compression of the spinothalamic tract, posterior column, and spinal roots can lead to changes in pain, temperature




Hoffman S Sign Positive Youtube



Cervical Myelopathy Hoffman Sign
A Systematic Review of the Utility of the Hoffmann Sign for the Diagnosis of Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Fogarty A, Lenza E, Gupta G, Jarzem P, Dasgupta K, Radhakrishna M Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18 Dec 1;43(23) doi /BRSThe Hoffmann sign is used by examiners assessing patients with symptoms of myelopathy (spinal cord compression) The test is done by quickly snapping or flicking the patient's middle fingernail The test is positive for spinal cord compression when the tip of the index finger, ring finger, and/or thumb suddenly flex in responseMyelopathy Brachialgia and cord syndrome radicular pain in the upper extremity along with motor and/or sensory longtract signs ref Complications of anterior cervical discectomy without fusion in 450 consecutive patients ref Lhermitte's sign Review with special emphasis in oncology practice ref Prevalence of Physical Signs in




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals




Hoffman S Sign What Do Positive And Negative Test Results Mean
Jul 01, 15 · Several clinical signs have been used as markers of cervical myelopathy – these include exaggerated deep tendon reflexes, Hoffman's reflex, the Babinski sign, increased tone, clonus, etc The Trömner and the Wazir hand myelopathy signs have also found to be very sensitive for detecting myelopathy at or above the C56 level 15Feb 17, 21 · During a standard neurological exam, the Hoffman sign is common, and a positive sign can aid in the diagnosis However, a 18 systematic review, with level 1 evidence, on the utility of the Hoffman sign for the diagnosis of degenerative cervical myelopathy found insufficient data to support the use of the exam alone to confirm or refute aJun 12, 18 · According to the Indian Journal of Medical Specialties, the Hoffman sign is more likely to occur in people with cervical myelopathy or injuries or damage to the cervical spine, which is the upper portion of the spine that affects the neck Takeaway People may have a positive Hoffman's sign yet have no other clinically significant problems




Hoffmann Sign Article




Positive Hoffman Sign In A Patient With Cervical Myelopathy Neurology Positivity Cervical
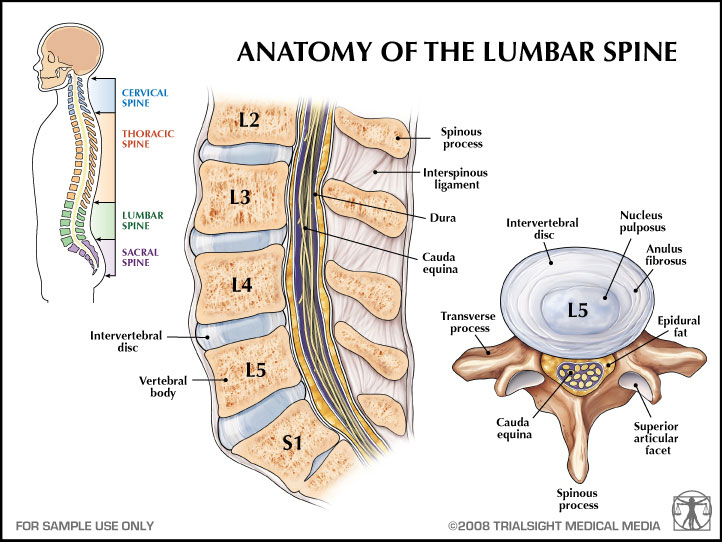
Cervical myelopathy is a form of myelopathy that involves compression of the spinal cord in the cervical spine (neck) Your cervical spine contains seven vertebrae (C1 to C7), with six intervertebral discs and eight nerve roots The spinal cord travels inside the vertebral column constructed from the front by vertebrae, cushioned by theUpper extremity hyporeflexia (lower cervical lesion) or hyperreflexia (upper cervical lesion with a positive Hoffman sign) and intrinsic muscular atrophy Differential Diagnosis The differential diagnosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy is quite broadOn physical examination he has 5 of 5 motor strength in all muscles groups in his upper and lower extremities, a bilateral Hoffman sign, bilateral 3 patellar reflexes, 3 beats of clonus on the right, and no clonus on the left




Cervical Myelopathy




The Method Of Eliciting The Reflexes A Eliciting The Hoffman S Download Scientific Diagram
Myelopathy or infection must also be sought Lhermitte sign (shocklike paresthesias occurring with neck flexion), difficulty walking, or bowel and bladder symptoms are suggestive of myelopathy or intramedullary pathology Any history of fever, chills, weight loss, or cancer should raise suspicion for tumor or infection5Analysis of combined data from 2/3 studies indicated that the Hoffman sign has a positive likelihood ratio of 22 (95% CI 1533) and a negative likelihood ratio of 063 (95% CI 0508) Conclusion A positive Hoffman alone is unlikely to lead to more than a small change in estimated probability of DCM as compared with the gold standard test (magnetic resonance imaging)Hoffman's sign can be a feature of myelopathy involving the cervical spinal cord It is a test performed by doctors during their neurological examination By holding a patient's hand so that it is weightless, and flicking the nail of their middle finger, a positive test (ie one suggesting central nervous disease) causes a reflex to make




Lil Bone Peep Hoffmann S Sign Upper Motor Neuron Test Perform By Flicking Or Tapping The Nail While Relaxed Sign If The Thumb Index Finger Reflexively Adduct Flex
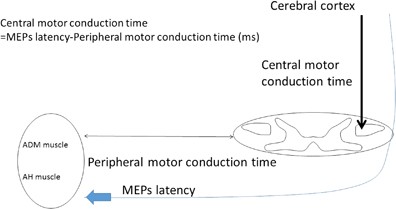



Characteristics Of C6 7 Myelopathy Assessment Of Clinical Symptoms And Electrophysiological Findings Spinal Cord
Mar 04, 15 · Diabetes may affect the typical physical findings associated with cervical spondylotic myelopathy, as coexisting diabetic neuropathy may dampen expected hyperreflexia and also produce nondermatomal extremity numbness Most large studies of surgically treated diabetic patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy have focused upon infectionWazir sign was observed and well reproducible in 54 out of 58 patients (93%) in Group 1, with three patients having positive myelopathy signs (Hoffman's sign, finger escape and ten second test) These patients showed moderate to severe stenosis z C5/6 on MR imaging The remaining four (6%) patients in Group 1 did not demonstrate anyFeb 21, 13 · Out of the five tests, the two that students have the most trouble with (and never see a positive sign) are the Hoffman's Test and Inverted Supinator Sign I find both of these to have high specificity values in my practice (which means if the test is positive, a high probability of an upper motor neuron disorder is present)




Cervical And Lumbar Degeneration Flashcards Quizlet




Hoffman S Sign Positive دیدئو Dideo
Myelopathy is an injury to the spinal cord due to severe compression that may result from trauma, congenital stenosis, degenerative disease or disc herniation The spinal cord is a group of nerves housed inside the spine that runs almost its entire length When any portion of the spinal cord becomes compressed or constricted, the resultingFeb 21, 17 · CCI often occurs with basilar invagination or ventral brainstem compression, the findings of which are dominated by pyramidal and sensory changes weakness of the limbs hyperreflexia and pathological reflexes (eg, Babinski, Hoffman's sign, absence of the abdominal reflex), paresthesias, and a plethora of other symptoms—including sphincterUpper motor neuron signs—weakness, spasticity, clumsiness, altered tonus, hyperreflexia and pathological reflexes, including Hoffmann's sign and inverted plantar reflex (positive Babinski sign) Lower motor neuron signs—weakness, clumsiness in the muscle group innervated at the level of spinal cord compromise, muscle atrophy, hyporeflexia, muscle hypotonicity or flaccidity,
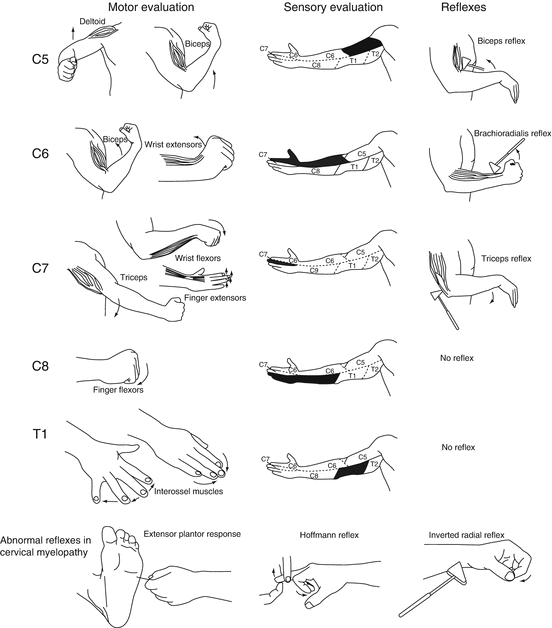



The Cervical Spine Springerlink




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The Bmj
Dec 03, 19 · Out of the five tests, the two that students have the most trouble with (and never see a positive sign) are the Hoffman's Test and Inverted Supinator Sign I find both of these to have high specificity values in my practice (which means if the test is positive, a high probability of an upper motor neuron disorder is present) So, here they areCervical myelopathy is a clinical syndrome that involves the disruption of neuronal impulses from the brain through the spinal cord, at the level of the cervical spine Due to the location of the signal interruption, the patient may experience symptoms related to the arms, hands, legs, bowel and bladder functions Cervical Myelopathy Read more about Symptoms, Diagnosis, TreatmentAug 13, 15 · Various studies have opined that a positive Hoffmann Sign highly correlates to the presence of cervical myelopathy It is accepted knowledge that a positive Hoffmann response can also indicate the presence of Central Nervous System (Brain) abnormalities, as




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Wayne Cheng Md Instructor




Hoffmann S Sign Test Cr Youtube




Positive Hoffman S Sign And Hyperreflexia With Cervical Spinal Stenosis Youtube



Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Natural History Clinical Presentation Current Diagnosis And Treatment Update Maeda International Journal Of Orthopaedics



Cervical Myelopathy And Lumbar Spondylolisthesis In Elderly Patients With Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Dish A Case Series Journal Of Orthopaedic Case Reports
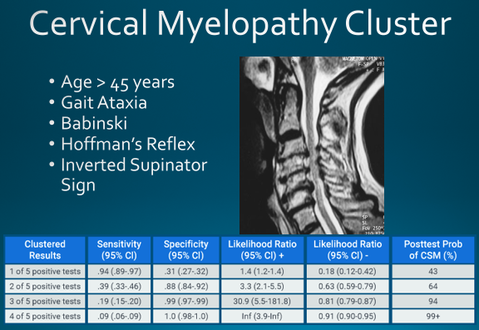



Blog Posts
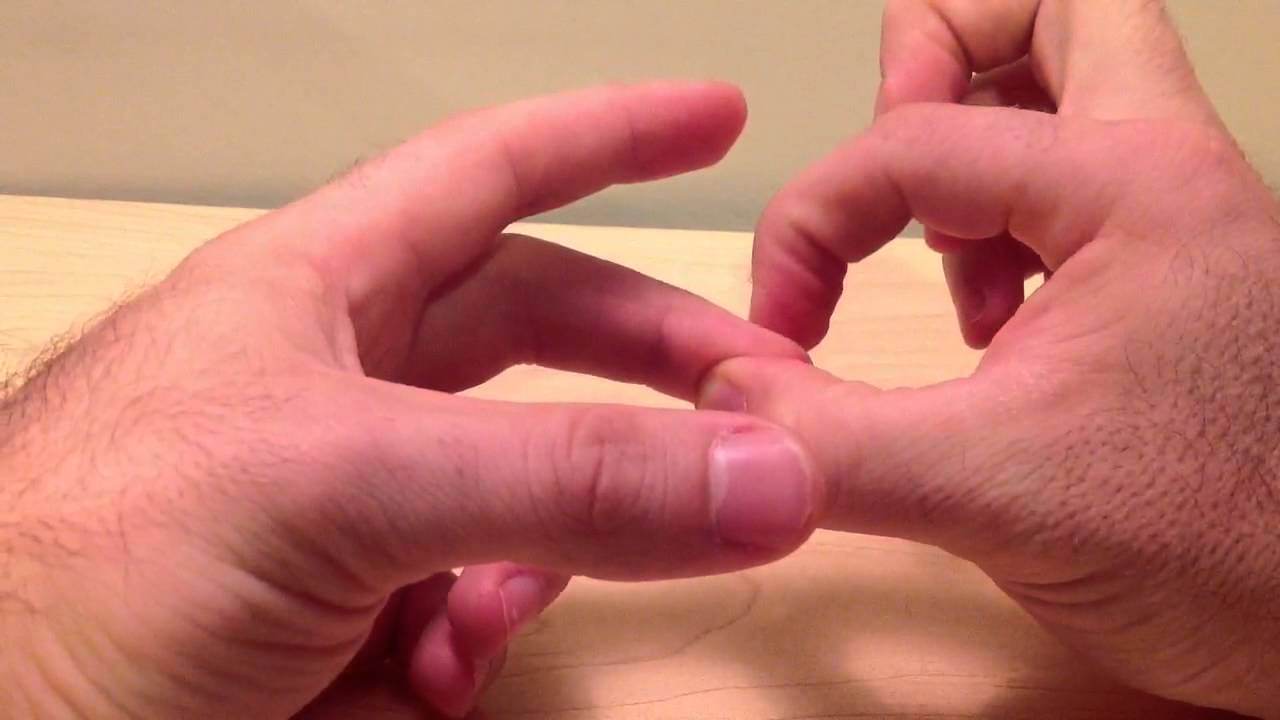



Hoffmann S Reflex Neurologyneeds Com




Congenital Malformed Posterior Arch Of Atlas With Fusion Defect A Case Of Developmental Canal Stenosis Causing Cervical Myelopathy Shah Journal Of Spine Surgery



Blog Posts




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Jim




Cervical Myelopathy Physiopedia



Neurological Signs In Medicine




Pdf Clinical Sign Revisited Hoffman S Sign




Cervical And Lumbar Degeneration Flashcards Quizlet




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada



History And Physical Examination Neupsy Key




Nw Surgical Research Foundation Conference Ppt Download




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08




Pdf Mimickers Of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Semantic Scholar




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Common Cause Of Spinal Cord Dysfunction In Older Persons American Family Physician




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Jim




Hoffmann S Sign Test Myelopathy Multiple Sclerosis



Myelopathy Physiopedia



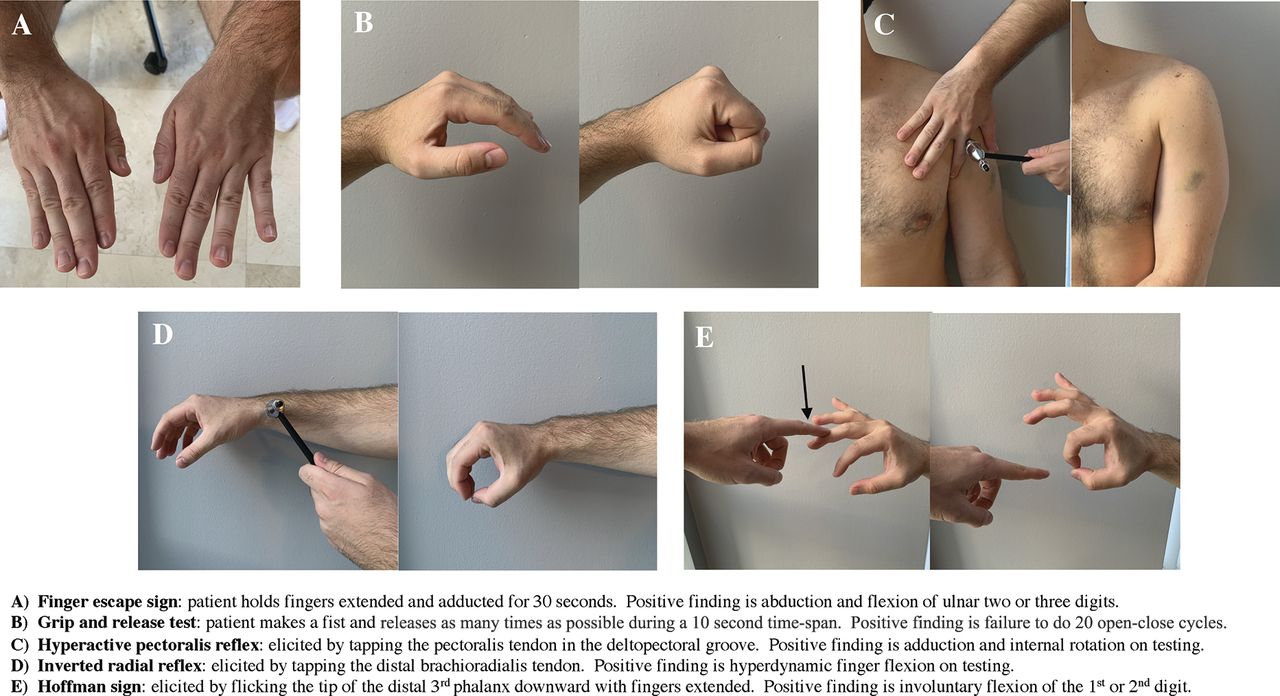
Cervical Myelopathy Physiopedia




Myelopathic Signs And Functional Outcome Following Cervical Decompression Surgery A Proposed Myelopathy Scale In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 24 Issue 6 16




Table 2 From Clinical Evidence For Cervical Myelopathy Due To Chiari Malformation And Spinal Stenosis In A Non Randomized Group Of Patients With The Diagnosis Of Fibromyalgia Semantic Scholar



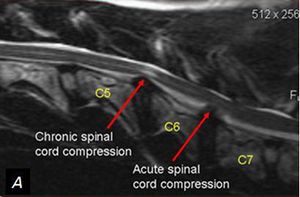
Ns Neurospine



Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08



Cervical Myelopathy And Lumbar Spondylolisthesis In Elderly Patients With Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Dish A Case Series Journal Of Orthopaedic Case Reports



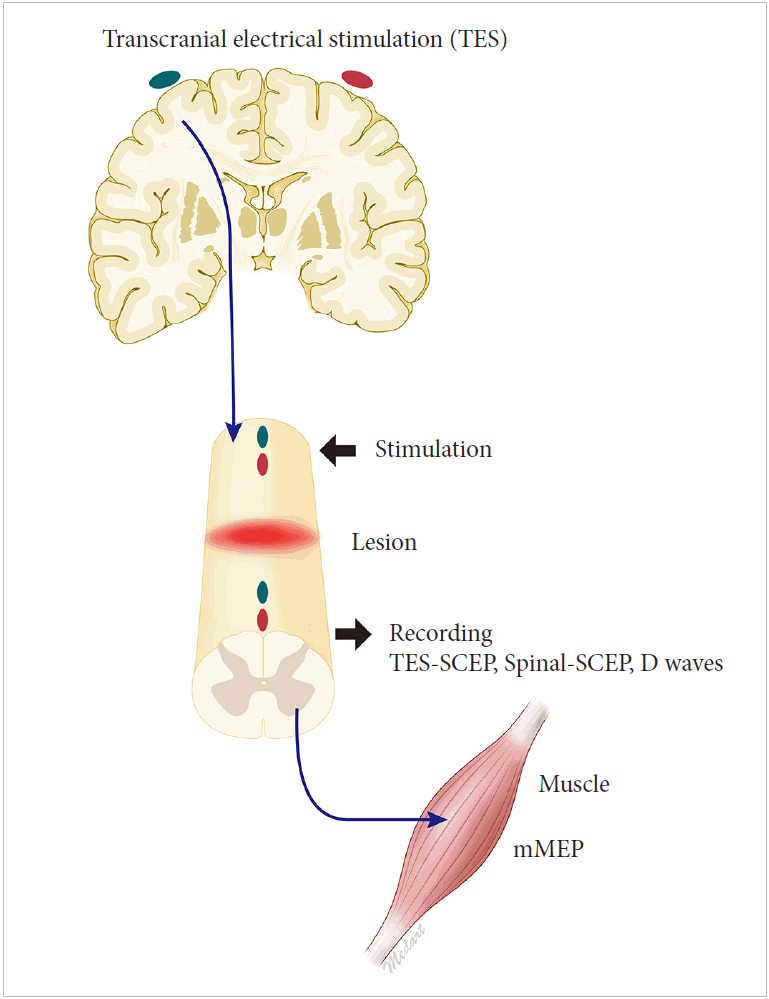
Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy A Guide To Diagnosis And Management American Board Of Family Medicine




Primary Care Management Of The Degenerative Spine Jim




What Does A Positive Hoffman Sign Mean Quora




Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada




Hoffmann S Sign Test Myelopathy Multiple Sclerosis
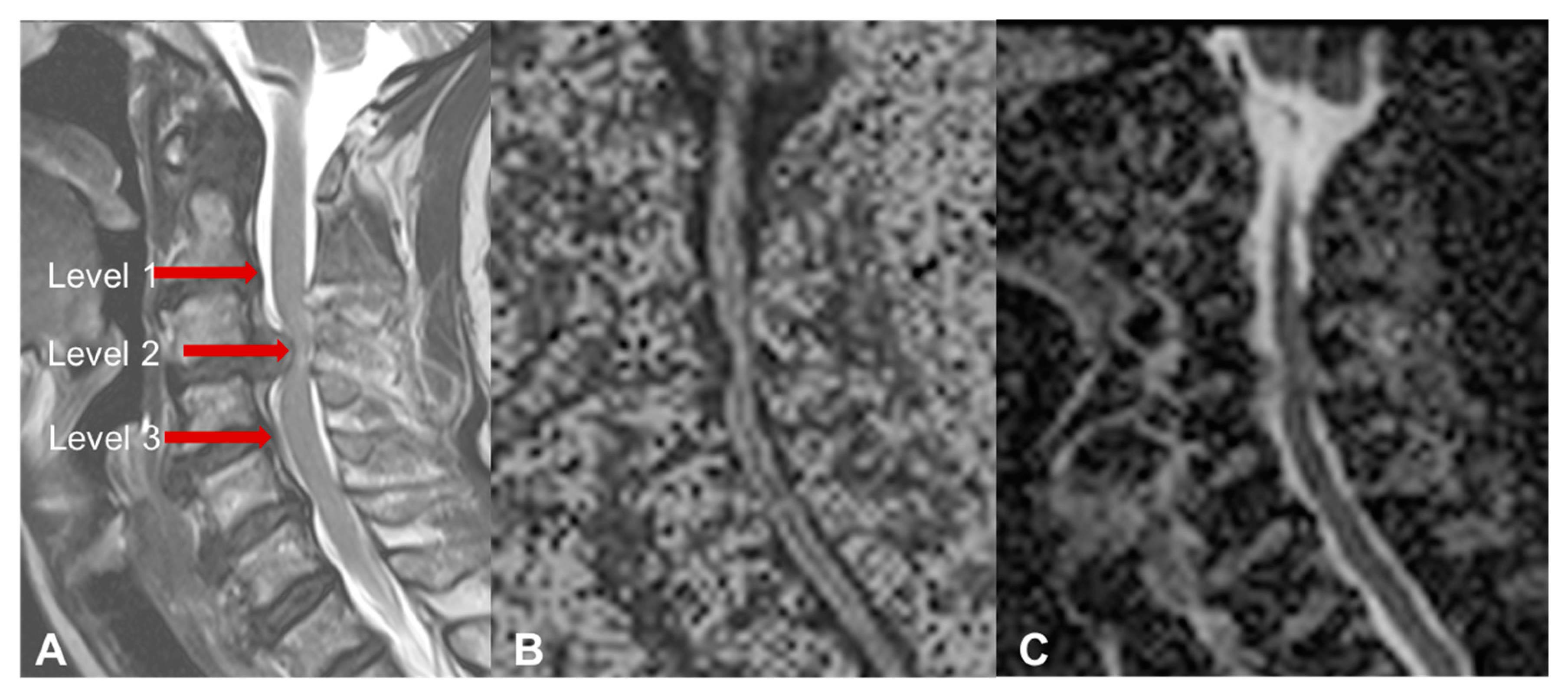



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy How To Identify The Best Responders To Surgery Html




Hoffman S Sign What Do Positive And Negative Test Results Mean




Hoffmann S Sign Or Reflex Upper Motor Neuron Lesion Youtube




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment




Traumatic Cervical Myelopathy Neupsy Key




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals




Myelopathy Arkansas Neurological Spine Disorders Arkansas Fayetteville Ar




Neurological Signs In Medicine




Hoffmann S Sign Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim Youtube




Predictors Of Symptomatic Myelopathy In Degenerative Cervical Spinal Cord Compression Kadanka 17 Brain And Behavior Wiley Online Library




Myelopathy Secondary To C5 C7 Synovial Cyst




Adult Cervical And Thoracic Spine Broadcastmed




Medicosnotes Com What Is Hoffman Reflex A Complete Guide




Cervical Myelopathy Presenting With An Acute Horner S Syndrome Sciencedirect
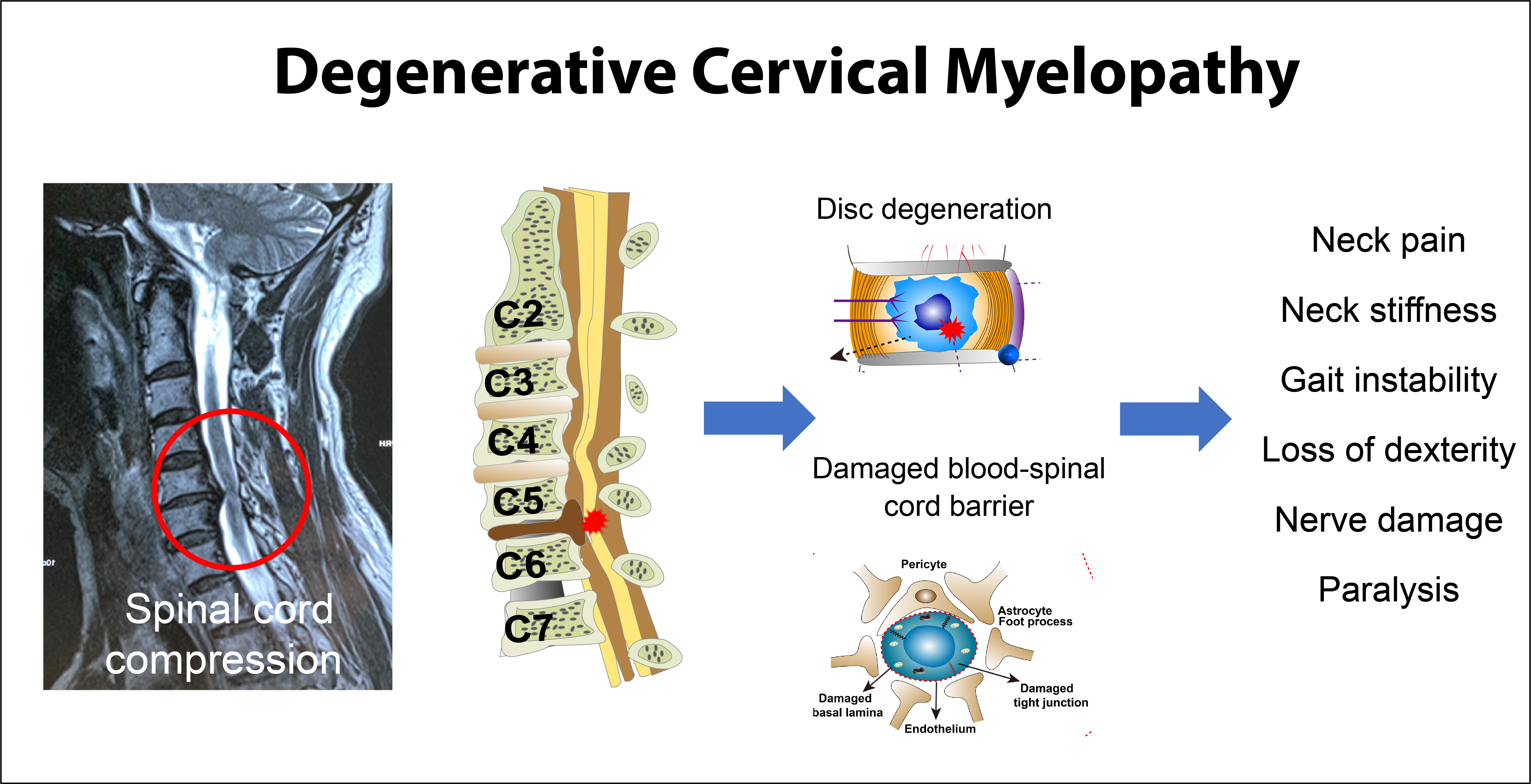



Jcm Free Full Text Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Insights Into Its Pathobiology And Molecular Mechanisms Html




Neurological Signs In Medicine




Approaching Neck Pain Mcp Ipa Lbp Task Force Ppt Download




Table 1 From Clinical Evidence For Cervical Myelopathy Due To Chiari Malformation And Spinal Stenosis In A Non Randomized Group Of Patients With The Diagnosis Of Fibromyalgia Semantic Scholar




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Ppt Video Online Download




C Spine T Spine And Cranial N Special Tests Flashcards Quizlet




Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Presenting As Mechanical Neck Pain A Case Report Manual Therapy




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment




Axial Neck Pain Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Recognition And Treatment Page 3




The Method Of Eliciting The Reflexes A Eliciting The Hoffman S Download Scientific Diagram
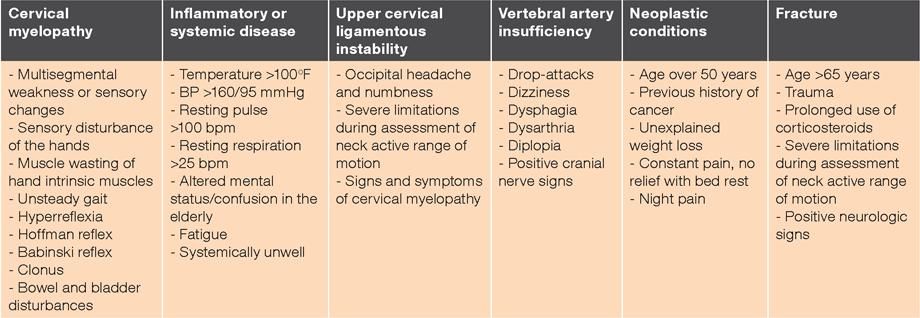



Csiro Publishing Journal Of Primary Health Care




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets




Clinical Spectrum And Importance Of Evaluation Systems In Degenerative Cervical Myeloradiculopathy Swaminathan G Muralidharan V Joseph Bv Indian Spine J




Cervical Myelopathy Spine Orthobullets



Cervical Spine Examination Orthopaedicprinciples Com
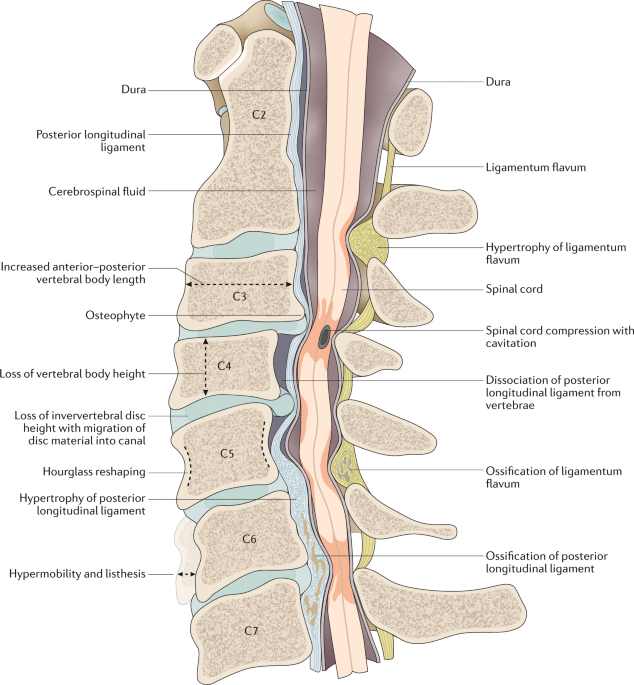



Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy Update And Future Directions Nature Reviews Neurology




Cervical Radiculopathy Myelopathy University Hospitals




Osteopathic Evaluation And Post Surgical Rehabilitation Approach In A Patient With Myelopathy And Tetraparesis Related To Cervical Ependymoma A Case Report Ostmed Dr




Cervical Radiculopathy And Myelopathy Wayne Cheng Md Instructor




Clinical Correlations Of Cervical Myelopathy And The Hoffmann Sign In Journal Of Neurosurgery Spine Volume 9 Issue 3 08




The Spine Clinics Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Clinical Scenarios Nanda A Renjith K R Mallepally A Prasath C S Shetty Ap Indian Spine J


